629. Accelerating polyester hydrolysis through blending with bio-based poly(4-hydroxyphenylacetate) multiblock copolymers
Matina Terzi, Virginia Celestre, Peter Tang, Jeppe Madsen, Anders E. Daugaard, EuroPolymerJ, (2025), DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2025.113841
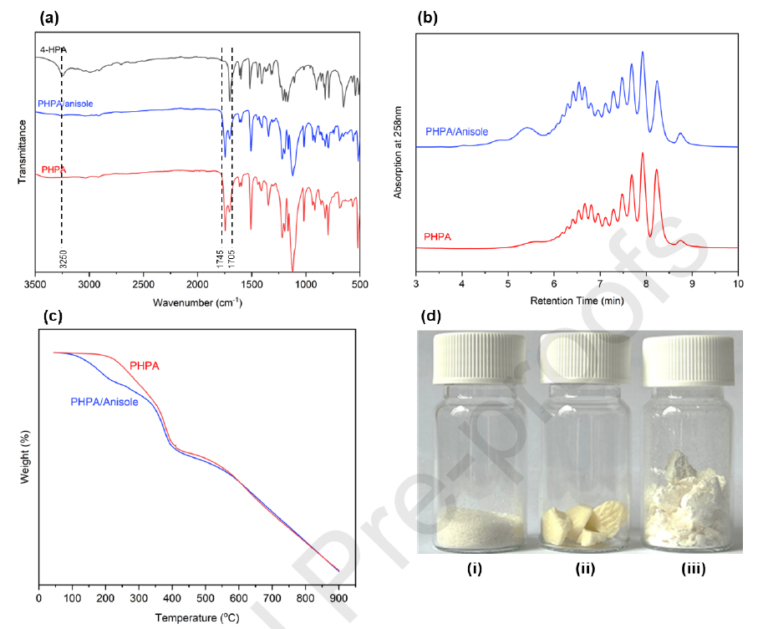
Poly(4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid), PHPA is a bio-based aromatic polyester synthesized by polycondensation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (HPA) in bulk. The liquid crystalline behavior of PHPA allows transesterification with commonly used polyesters like PLA, PETG, and PCL at relatively low temperatures to give multiblock copolymers that have a high blending compatibility with the parent polyester. The resulting polymer blends with PLA exhibit accelerated hydrolytic degradation compared to pristine PLA and a 36% decrease of the flexural modulus of the blends of PLA containing up to 10 % of PHPA-PLA multiblock copolymers.